In modern vehicles, the automobile electrical system is essential for starting the engine and powering all electrical components. Without it, even a mechanically sound car cannot operate. Therefore, understanding its basics becomes important for every learner. In this blog, we will provide a clear and concise explanation of the battery, alternator, starter motor, and wiring system, step by step.
What Is an Automobile Electrical System?
Simply put, the automobile electrical system is a network of electrical components that generate, store, control, and distribute electrical power inside a vehicle.
In general, this system performs three main functions:
- Power generation
- Power storage
- Power distribution
Moreover, it converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy and then supplies it wherever required.
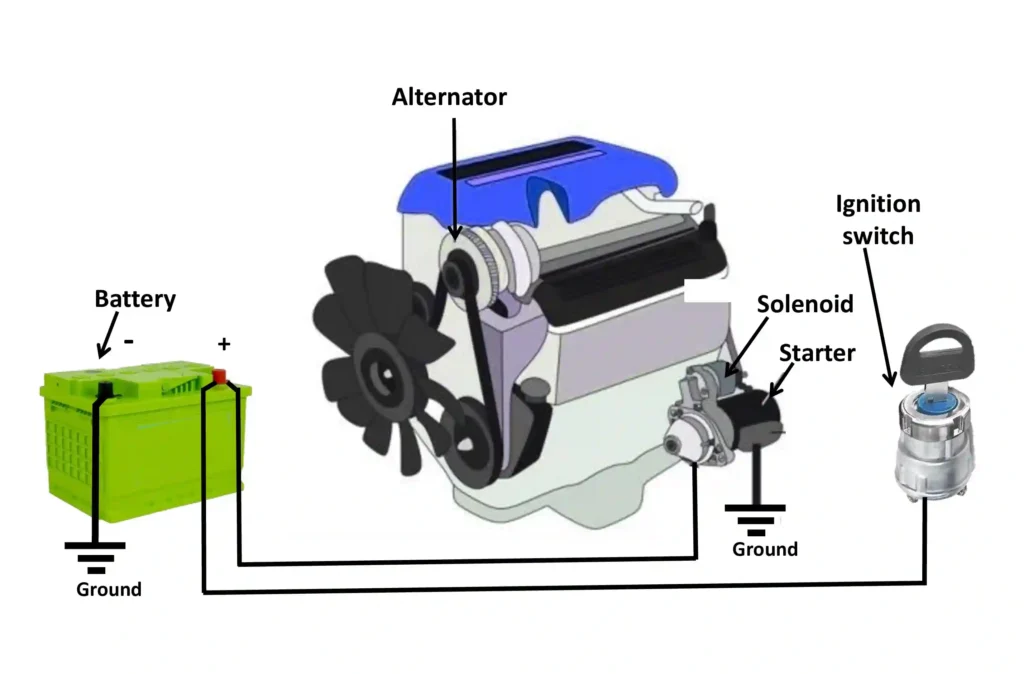
Main Components of an Automobile Electrical System
Basic automobile electrical system components
- Battery – Power source
- Alternator – Charging system
- Starter Motor – crank the engine to start
- Wiring & Circuits – Power distribution
- Fuses and Relays– Protection & control
- Switches and Loads– operate devices like headlamp, horn, etc
These are pure electrical components, which can operate without an ECU/ECM. For example, Old tractors, old trucks, and old bikes have no ECM.
Advanced Automobile Electronic Control System components
(Covered in the next blog)
- ECM / ECU – Controls engine operation by processing sensor data
- Sensors (CKP, CMP, VSS, etc.) – Monitor engine conditions and send signals to the ECM
- Actuators (Injectors, fuel pump relay, IAC, etc.) – Perform actions as commanded by ECM
1. Battery: Heart of the Automotive Electrical System
The battery is the primary source of electrical power in a vehicle when the engine is not running. It stores electrical energy in chemical form and supplies it as direct current (DC).
Typically, most passenger vehicles use a 12-volt lead-acid battery.
Functions of a Car Battery
The battery performs several important functions, such as:
- Providing power to start the engine
- Supplying electricity to lights and accessories when the engine is off
- Stabilizing voltage in the electrical system
- Supporting electronic control units (ECUs)
- Therefore, without a healthy battery, the vehicle cannot start.
Types of Automobile Batteries
Although lead-acid batteries are most common, there are different types used in vehicles:
- Flooded Lead-Acid Battery
- Maintenance-Free Battery
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Battery
- Lithium-Ion Battery (mostly in EVs and hybrids)
Each type has its own advantages, depending on vehicle design and usage.
Every battery has: Positive terminal (+) & Negative terminal (–)
The Negative terminal (–) is connected to the vehicle body (ground). As a result, the vehicle chassis acts as a return path for current flow.
2. Alternator: The Power Generator
Once the engine starts, the alternator becomes the main source of electrical power. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. Slip-ring alternators are widely used in automobiles.
Although the alternator produces AC (Alternating Current), it is converted into DC (Direct Current) using rectifier diodes, because vehicle systems require DC power.
Thus, it ensures an uninterrupted power supply during driving.
Functions of an Alternator
- Supplies electricity to all electrical components while the engine is running
- Recharges the battery continuously
Thus, it ensures an uninterrupted power supply during driving.
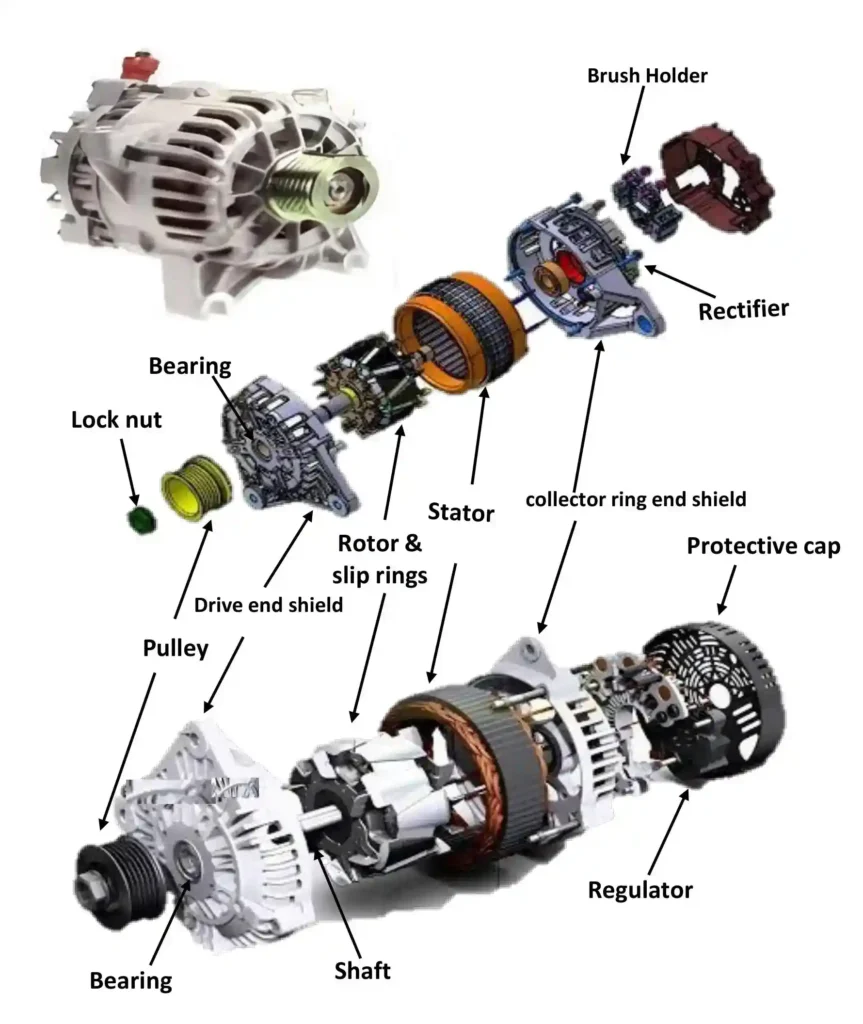
Main Parts of an Alternator
An alternator consists of:
- Rotor
- Stator
- Slip rings
- Carbon brushes
- Rectifier (diodes)
- Voltage regulator
Each part works together to maintain a stable voltage, which ranges from approximately 13.5 to 14.5 volts.
What Happens If the Alternator Fails?
If the alternator fails:
- The battery will not charge
- Electrical components will stop working gradually
- The vehicle may stall while driving
Therefore, a healthy alternator is essential.
3. Starter Motor: The Engine Cranker
The starter motor is a high-power electric motor used to crank the engine during starting. It draws a large amount of current from the battery for a short time.
Once the engine starts, the starter motor automatically disengages.
Working Principle of Starter Motor
The operation of a starter is simple. When the ignition key or bottom is depressed, the transmission should be in the park or neutral position. In this instance, the battery voltage activates the solenoid by passing through the starter control circuit.
The solenoid powers the starter motor, which helps to move the starter gear forward so that it meshes with the engine flywheel. Since the flywheel is mounted on the engine’s crankshaft, when the starter motor turns, the flywheel & crankshaft also rotate. When the engine starts, the system disengages from the flywheel
Types of Starter Motors
The main types of starter motors are:
- Direct drive starter motor (DD)-used in old models
- Planetary gear (PLGR)
- Permanent magnet gear reduction (PMGR)
- Permanent magnet direct drive (PMDD)
- Off-set gear reduction (OSGR)-commonly used in modern vehicles
.
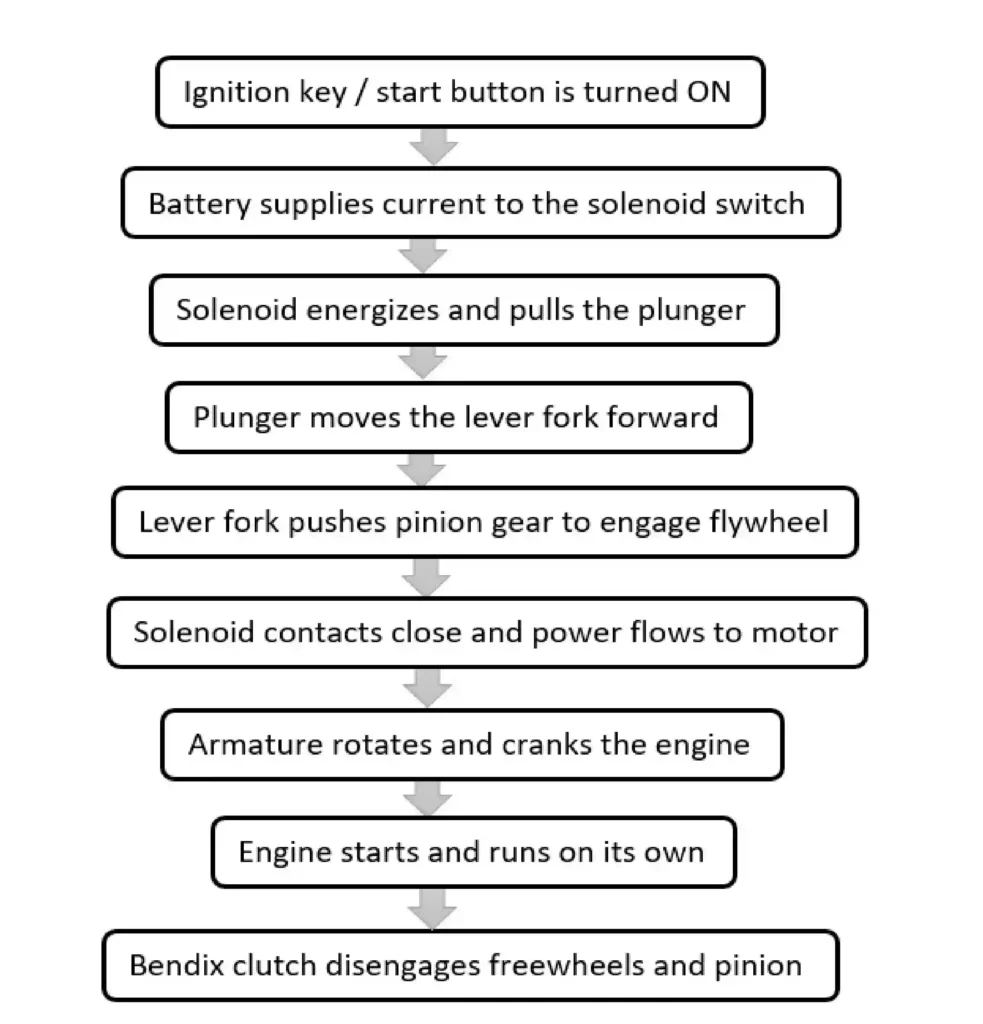
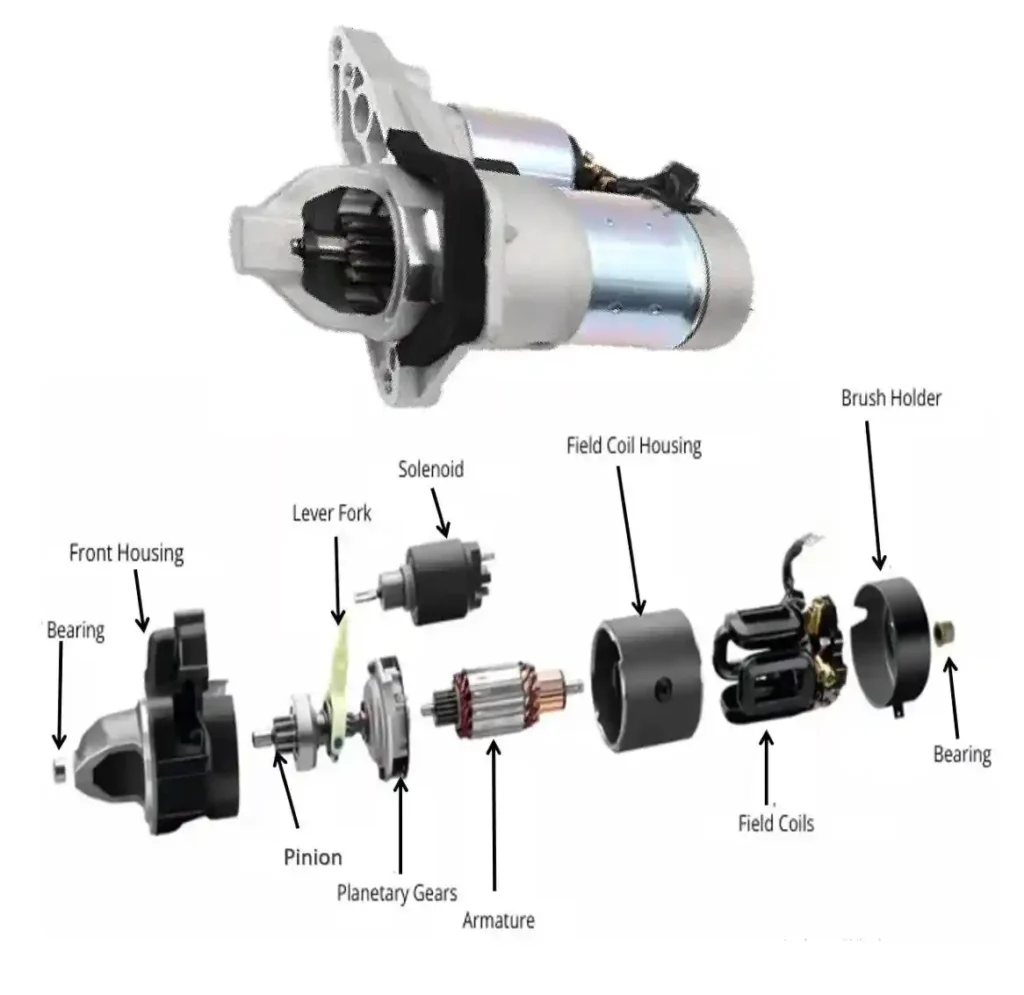
Components of a Starter Motor
- Armature
- commutator
- Field coils/permanent magnets
- Solenoid switch
- brushes
- plunger
- lever fork
- Pinion gear
- Overrunning/starter/Bendix clutch
All these components must work perfectly for the engine to start smoothly.

4. Wiring System: The Electrical Pathway
The wiring system is the network of wires that connects all electrical components in a vehicle. It ensures a safe and controlled flow of electrical current.
In other words, wiring is the circulatory system of the automobile’s electrical setup.
Types of Wires Used in Vehicles
Automotive wires are specially designed to:
- Handle heat
- Resist vibration
- Withstand moisture and oil
- Common wire types include:
- Copper stranded wires
- PVC insulated wires
- Heat-resistant automotive cables
Wiring Harness Explained
Instead of loose wires, vehicles use a wiring harness, which is a bundled set of wires wrapped together. This improves:
- Safety
- Organization
- Ease of maintenance
As a result, troubleshooting becomes much easier.
Types of Wiring & Harnesses
- Standard Wiring Harness-Connects major vehicle electrical systems using color-coded and bundled wires.Used in Headlights, horn, indicators, ignition system.
- Engine Wiring Harness- Links engine sensors, actuators, and the Engine Control Unit (ECU).used in Fuel injectors, ignition coils, throttle position sensor (TPS), crankshaft sensor.
- Chassis Wiring Harness-Supplies power and signals to body and chassis-mounted components.Used in Exterior lights, wipers, horn, ABS wheel speed sensors.
- Door Wiring Harness-Transfers power and control signals between the vehicle body and door systems.used in Power windows, central locking, side mirrors, door speakers.
- Instrument Panel / Interior Wiring Harness- Connects dashboard electronics, controls, and comfort systems.Used in Instrument cluster, infotainment system, switches, HVAC controls.
- Battery & Power Distribution Harness-Distributes main electrical power from the battery to high-current circuits.used in Starter motor, alternator, main fuse box, high-power electrical accessories.
Key Functions of Wiring System
- Power Distribution: Supplies electrical energy to all vehicle components.
- Signal Transmission: Carries sensor data and control signals to and from the ECU.
- Protection & Organization: Prevents short circuits and makes maintenance easier.
- Durability: Insulated and protected wiring resists heat, moisture, and vibration.
Colour Coding in Automobile Wiring
To avoid confusion, wiring uses standard colour codes:
- Red – Power supply
- Black – Ground
- Yellow – Ignition
- Blue – Lighting
- Green – Sensors or signals
However, colour standards may vary slightly by manufacturer.
5. Fuses – Circuit Protection Device
A fuse breaks the circuit when current exceeds a safe limit, preventing damage to components, wiring, or fire hazards.
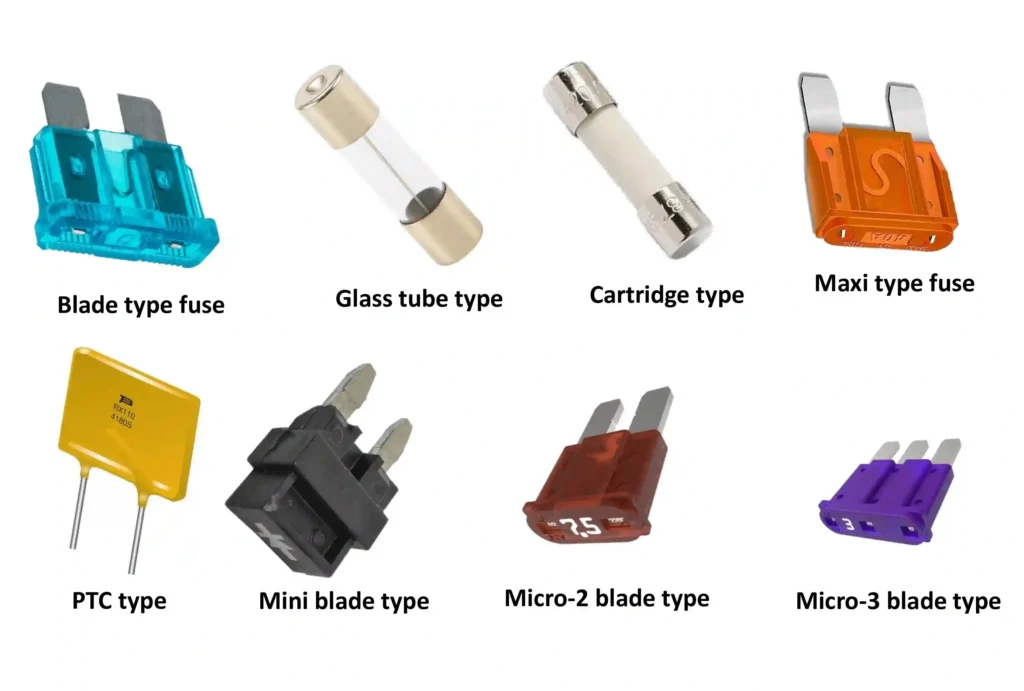
Types of Fuses
1. By Fuse Technology
- Blade Fuse – Plastic body with metal strip
- Glass Tube Fuse – Cylindrical glass with a metal strip
- Cartridge Fuse – High-current industrial type
2. By Blade Fuse Size
- Mini Blade – Compact low-amp fuse
- Micro Blade – Ultra-compact low-amp fuse
- Maxi Blade – High-amp fuse
3. By Function / Protection
- Standard Fuse – Overcurrent protection
- Resettable / PTC Fuse – Self-resetting overload protection
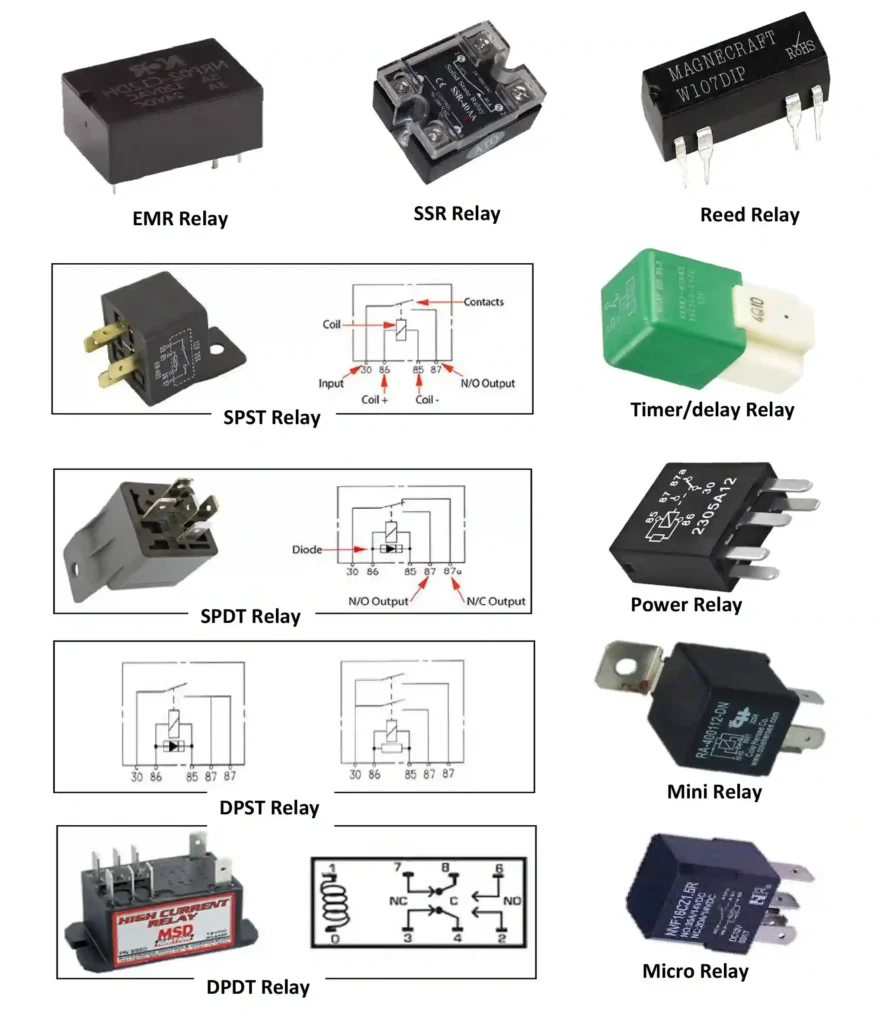
6. Relays – Electrical Control Switches
A relay is an electrically operated switch that allows a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit safely, increasing switch life and reducing wiring complexity.
Types of Relays
1. By Operating Technology
- EMR(Electromechanical Relay) – Mechanical contact relay
- SSR(Solid-State Relay) – Electronic contactless relay
- Reed Relay – Low-current signal relay
2. By Contact Arrangement
- SPST(Single Pole Single Throw) – ON/OFF contact
- SPDT(Single Pole Double Throw) – Changeover contact
- DPST(Double Pole single Throw) – Dual ON/OFF contact
- DPDT(Double Pole double Throw) – Dual changeover contact
3. By Function / Application
- Power / Load Relay – High-current switching
- Timed Relay – Time-delay switching
4. By Physical Size
- Micro Relay – Ultra-compact type
- Mini Relay – Compact type
DC Power in Automobiles
All automobile electrical systems operate on direct current (DC). Although the alternator generates AC, it is immediately converted to DC.
DC is preferred because it provides a stable voltage, which is essential for electronic components and sensors.
Common Electrical Problems in Vehicles
| Electrical Problem | Common Symptom | Possible Cause | Basic Solution |
| Weak / Dead Battery | Engine not starting | Battery discharged or aged | Recharge or replace the battery |
| Alternator Failure | Battery warning light ON | No charging from the alternator | Repair or replace the alternator |
| Starter Motor Fault | Clicking sound, no crank | Solenoid or motor wear | Inspect the starter motor |
| Blown Fuse | Sudden circuit failure | Overload or short circuit | Replace fuse (same rating) |
| Faulty Relay | Device not switching ON | Burnt relay contacts | Replace relay |
| Loose Battery Terminals | Intermittent power loss | Corrosion or loose clamps | Clean and tighten terminals |
| Damaged Wiring | Random electrical faults | Broken or shorted wires | Repair or replace wiring |
| Poor Grounding | Flickering lights | Loose or rusty ground | Clean and secure ground |
| Sensor Failure | Check engine light | Incorrect sensor signal | Test and replace the sensor |
| ECU Malfunction | Multiple warning lights | Voltage surge or moisture | ECU diagnosis/repair |
| Lighting System Fault | Headlamp not working | Blown bulb or fuse | Replace the bulb or fuse |
| Power Window / Lock Issue | No response from the switch | Motor or switch failure | Repair the motor or switch |
| Horn Not Working | No horn sound | Fuse, relay, or switch fault | Check the horn & its circuit |
| Instrument Cluster Issue | Gauges not working | Wiring or sensor issue | Inspect connections |
| Parasitic Battery Drain | battery drains overnight | Faulty relay or accessory | Identify and fix the drain |
Importance of Proper Earthing (Grounding)
Proper grounding ensures:
- Stable voltage
- Reduced electrical noise
- Safe operation of components
In automobiles, the negative battery terminal is grounded to the chassis, which acts as a common return path.
Maintenance Tips for the Auto-Electrical System
To keep the system healthy:
- Check battery terminals regularly
- Inspect wiring for damage & connections.
- test fuses & relays.
- Keep the battery charged.
- ensure proper grounding.
- Protect components from moisture.
- Check the alternator output.
- Replace weak batteries on time
- Keep the alternator belt properly tensioned
- Avoid overloading electrical accessories
As a result, the electrical system will remain reliable and long-lasting.
Future of Auto-Electrical Systems
With the rise of:
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Hybrid technology
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
Automobile electrical systems are becoming more complex and powerful. High-voltage systems, smart wiring, and digital control are shaping the future.
The automobile electrical system is the backbone of modern vehicles. Therefore, understanding these basics not only helps in troubleshooting but also improves vehicle safety, efficiency, and performance.
If you are a student, technician, or automobile enthusiast, mastering these fundamentals is the first step toward advanced auto-electrical knowledge.
Read about Electricity & its flow explained simply