A Pre-Engineered Building (PEB) is a steel structure in which all components are designed, fabricated, and pre-engineered in a factory and then assembled at the site using bolted connections.
As a result, construction becomes faster, economical, and highly accurate.
Pre-Engineered Building (PEB) Components
Understanding PEB components is essential before learning its benefits and uses. Therefore, below is a step-by-step classification of all Pre-Engineered Building components.
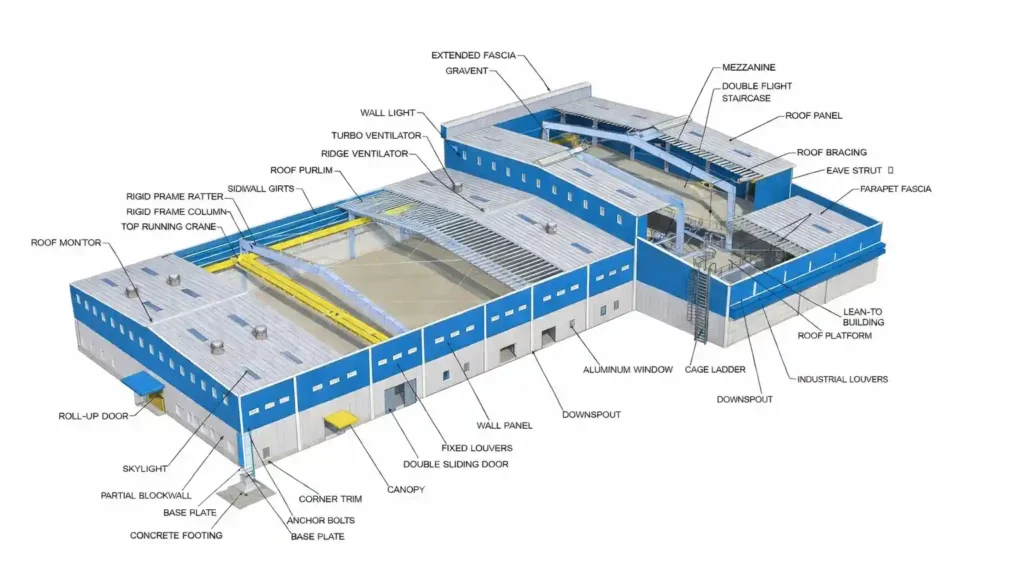
1. Primary Structural Components
Columns
- Vertical load-carrying members
- Transfer dead, live, wind, and seismic loads to the foundation
Rafters
- Horizontal or sloped members
- Support roof loads and connect columns
2. Secondary Structural Components
Purlins
- Support roof sheeting
Girts
- Support wall cladding
Eave Struts
- Connect the roof and wall at the eave level
Sag Rods
- Prevent buckling of purlins and girts
Tie Rods / Flange Bracing
Maintain spacing and alignment
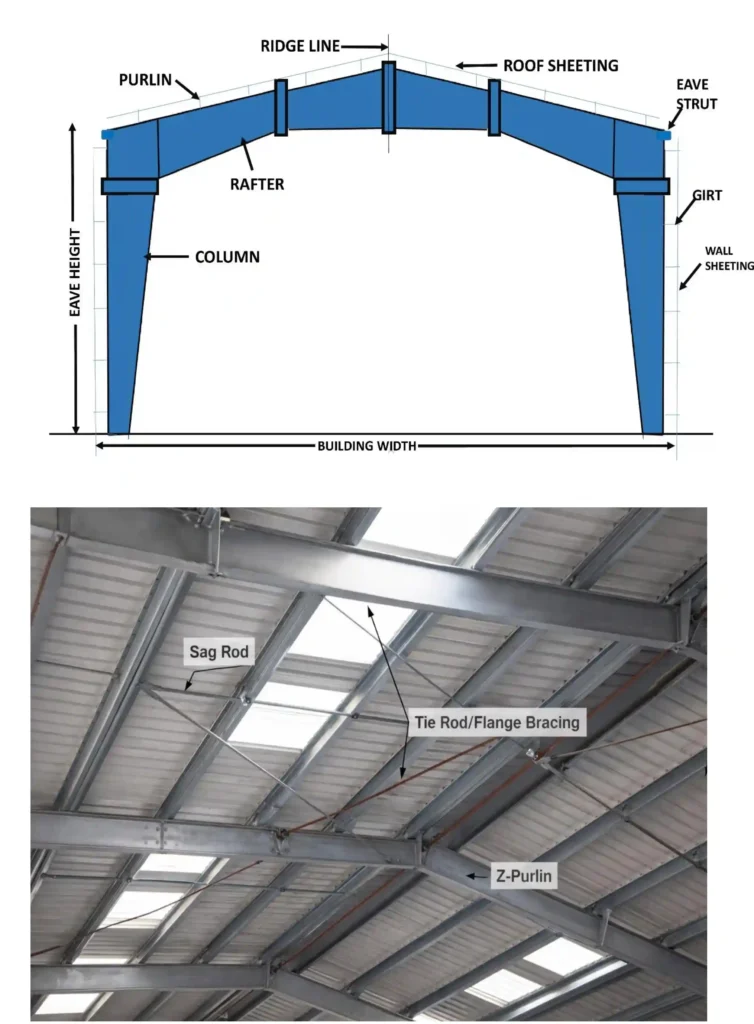
3. Bracing System
Rod Bracing
- Resists lateral loads
Cable Bracing
- Provides flexible stability for long spans
There are many other types of bracing, like channel bracing, angle bracing, etc
4. Roof System Components
Roof Sheets
- Weather protection
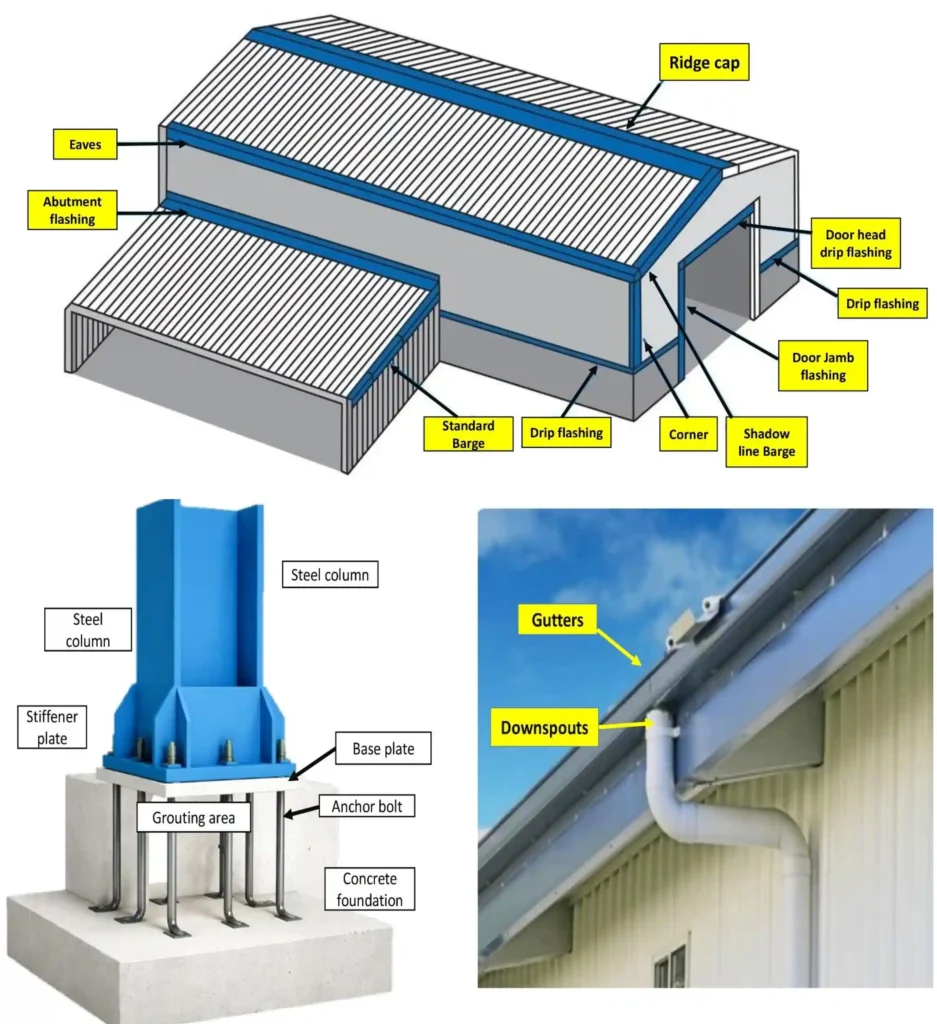
Ridge Cap
- Seals the roof ridge
Skylights / Roof Lights
- Natural daylight entry
Turbo Ventilators
- Heat and air exhaust
Gravity ventilator/GR Vent
- a passive ventilator that removes hot air naturally.
Roof Insulation
Thermal and sound control
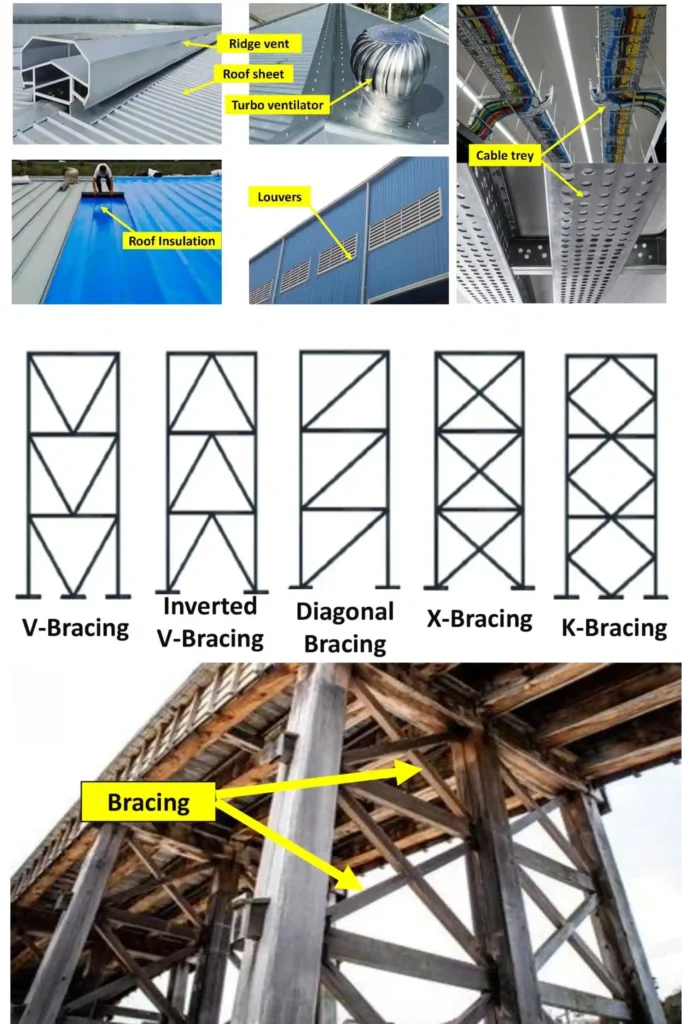
5. Wall System Components
Wall Cladding Panels
- External enclosure
Louvers
- Natural ventilation
Flashings (Corner, Eave, Trim)
- Prevent water leakage
Parapet Wall
- Architectural finish and safety
6. Openings and Access Systems
Doors
- Sliding doors, Rolling shutter doors, Personnel doors
Windows and Ventilators
- Light and airflow
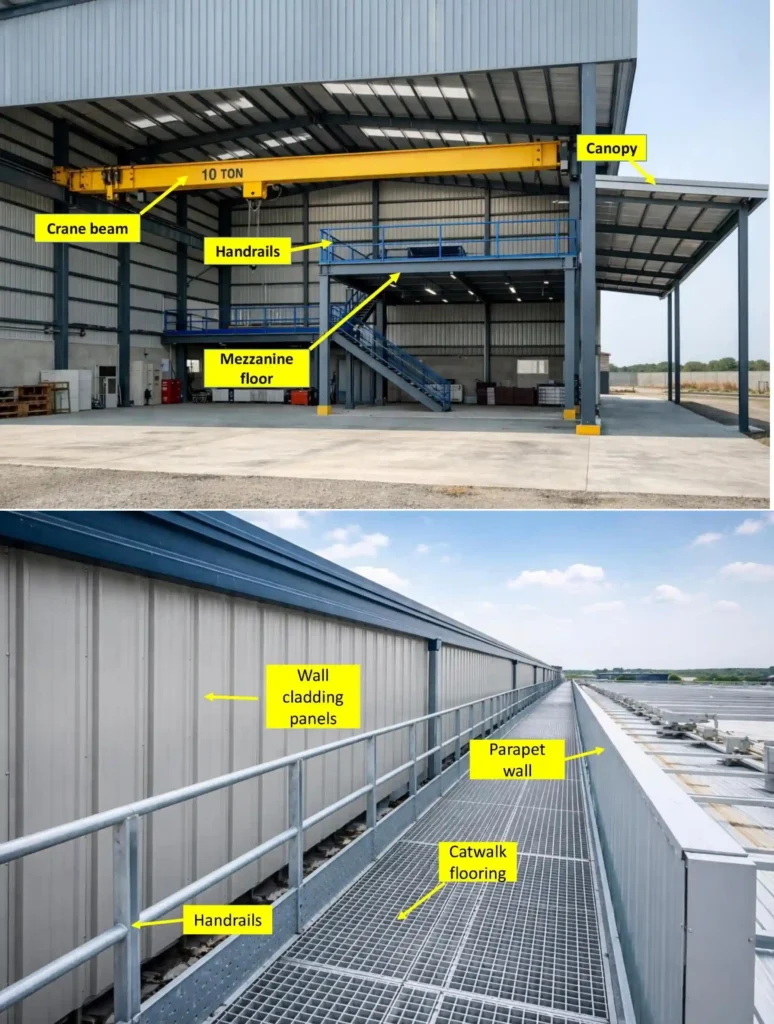
7. Industrial & Add-On Components
Crane Beams
- Support overhead cranes
Mezzanine Floors
- Additional usable floor space
Canopies
Covered external working areas
8. Drainage System
Gutters
- Collect rainwater
Downspouts
- Safe water discharge
9. Fire Protection Components
- Fire-resistant paint or coating
- Sprinkler systems and fire exit provisions
10. Electrical & Utility Provisions
Cable Trays
- Electrical routing
Lighting and HVAC Supports
- Utility installations
11. Surface Protection System
Primer Coating
- Corrosion protection
Final Paint / Galvanizing
- Long-term durability
12. Foundation Components
Base Plates
- Column-foundation connection
Anchor Bolts
- Load transfer to the foundation
Grouting
- Uniform load distribution
13. Maintenance & Safety Accessories
Catwalks
- Roof access
Ladders
- Vertical maintenance access
Handrails and Safety Cages
Worker safety
Advantages of Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB)
- Faster construction time
- Optimized steel usage
- Lower project cost
- Lightweight yet strong structure
- Reduced foundation requirement
- Factory-controlled quality
- Low maintenance
- Energy-efficient construction
- Easy future expansion
- Resistance to wind and seismic loads
- Environment-friendly material
- Large column-free spans
Applications of Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB)
- Industrial sheds and factories
- Warehouses and logistics centers
- Cold storage facilities
- Commercial buildings and showrooms
- Aircraft hangars
- Sports halls and indoor stadiums
- Educational and institutional buildings
- Labor camps and prefab housing
- Metro depots and railway workshops
- Power plants and substations
- Parking sheds and garages
- Exhibition and convention halls
Read about Basic Mechanical Components and Their Functions